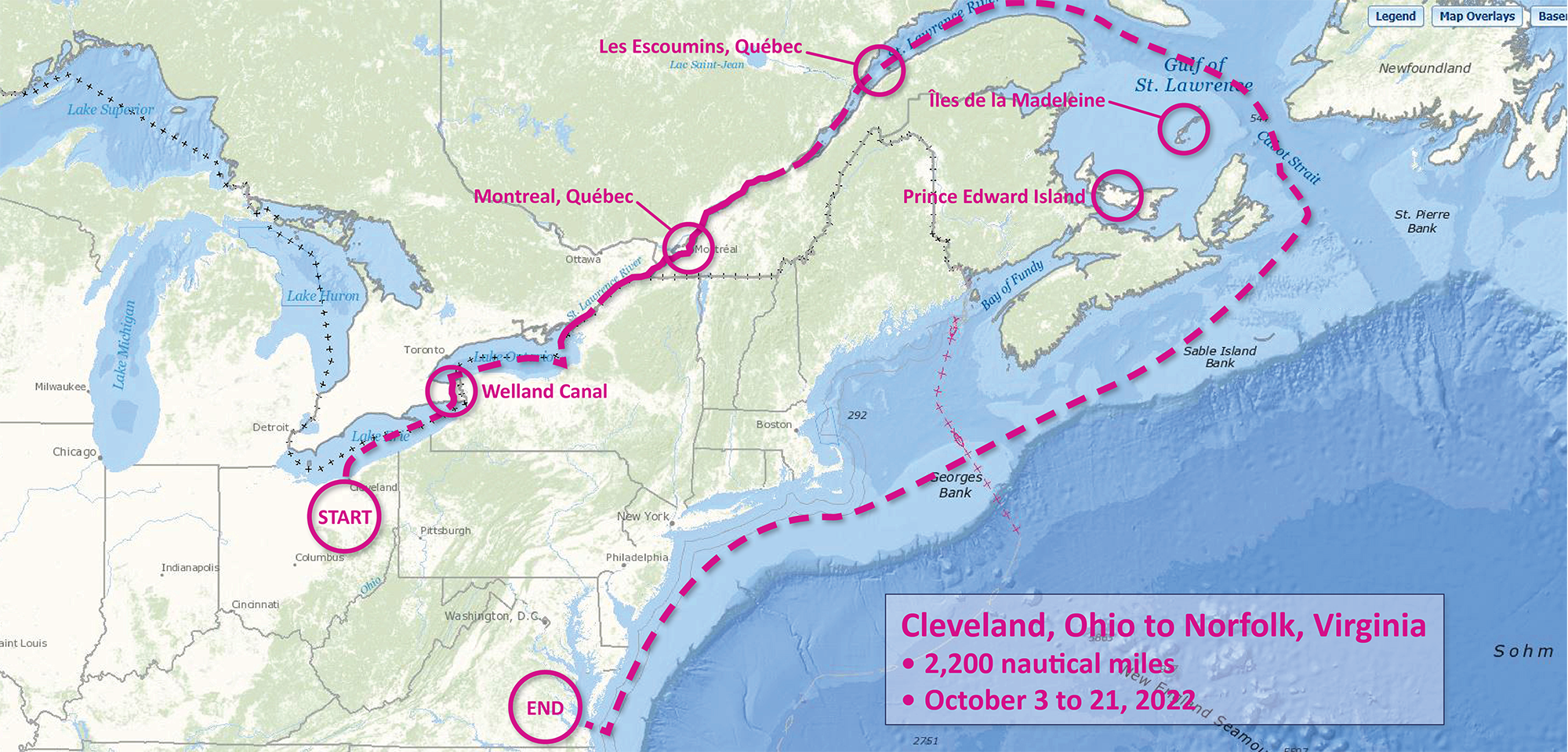
Although NOAA has a significant presence in the Great Lakes, this is the first time a white-hulled NOAA hydrographic ship has deployed there since the early 1990s. As a result of survey work in the Great Lakes, NOAA Ship Thomas Jefferson surveyed 450 square nautical miles of lake bottom in Lake Erie – an economically important and ecologically sensitive region. The ship also surveyed 274 square nautical miles in Lake Ontario in October. In both lakes, there were 42 confirmed and new shipwrecks identified along with 22 additional features!
Continue reading “NOAA Ship Thomas Jefferson completes productive field season in the Great Lakes”Conducting survey operations with Coast Survey’s navigation response teams
Strategically placed around the country, NOAA’s navigation response teams―30-foot survey vessels with a three-person survey team―maintain emergency readiness while checking chart accuracy in changing ports and harbors. Navigation response teams work day-to-day in ports and harbors, collecting data to update the nation’s nautical charts. They measure depths, locate obstructions, report dangers to navigation, and update features for safe navigation. Whether there is a need to investigate wrecks, check for suspected shoals, conduct surveys for coastal management, or work with other federal agencies to support homeland security, Coast Survey’s navigation response teams have the expertise to get the job done safely and efficiently.
Continue reading “Conducting survey operations with Coast Survey’s navigation response teams”Capturing scenes from hydrographic surveying
There are many benefits to working on a hydrographic survey project for NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey. Some would say having the opportunity to visit amazing landscapes, work with talented people, and collect important environmental data are just a few of them. Recently, Coast Survey’s Hydrographic Surveys Division hosted an internal photo contest inviting employees and contractors to submit images in the categories of Ships and Boats, Landscapes, People, and Data. On this Earth Day 2020, we thought we would share our contest winners with you.
Continue reading “Capturing scenes from hydrographic surveying”NOAA in the Great Lakes supports inter-agency search for WWII aircraft
Did you know that there are about 120 World War II era aircraft lying at the bottom of Lake Michigan? The Navy used these aircraft to train and certify pilots to take off and land from aircraft carriers during World War II. U.S. Naval operations along Lake Michigan, one of the Great Lakes, began in 1923. Between 1923 and 1942, operations expanded as the Navy built hangars, airfields, and landing strips across the village of Glenview, Illinois. By 1942, the Navy had a robust presence on the shores of Lake Michigan. With the U.S. entrance into World War II, the Navy needed a location to train carrier pilots. The growing threat of enemy vessels and mines along the Pacific and Atlantic coastlines and an already strong Naval presence in the area made Lake Michigan the safest location for carrier training.
Continue reading “NOAA in the Great Lakes supports inter-agency search for WWII aircraft”NOAA Ship Fairweather in western Alaska: A season of searching and survey
By ENS Linda Junge
NOAA Ship Fairweather has been busy during the last couple months. Three major activities have broken up the peak summer months of this field season. Continue reading “NOAA Ship Fairweather in western Alaska: A season of searching and survey”
Hydro on the Great Lakes: preserving American history
By Ensign Max P. Andersen
Formed by retreating ice sheets over 14,000 years ago, the Great Lakes have long represented one of the most valuable fresh water resources in North America. They contain more than one-fifth of the world’s supply of fresh surface water, and the vast size is easily visible from space. From Native American hunting routes to French fur-trade exploration to influential battles in the War of 1812, the Lakes have proved a key platform for numerous historical events that shaped the development of the country.
Uniquely, these bodies of water served as the gateway to connect the booming production of an expanding population in the Midwest from 1825 to 1925. During this time, a broad range of wooden, sailing, and steam-powered ships trekked across the lakes, carrying coal, grain, and passengers. Due to unpredictable weather conditions, fire, ice, high-traffic areas, and an ever-increasing pressure to meet shipping quotas, hundreds of ships were lost in collisions and accidents. These incidents have earned this period the nickname “Shipwreck Century.” Today, the history of the “Shipwreck Century” is presented at Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary’s visitor’s center, the Great Lakes Maritime Heritage Center, in Alpena, Michigan.
Thunder Bay is located in Lake Huron, near one of the most historically dangerous areas of navigation in the Great Lakes. The sanctuary covers 4,300 square miles. In this area, over 200 shipwrecks are known to exist, and 92 have been discovered and accurately charted. The staff provides continual archaeological monitoring to ensure the preservation of the sites.
Continue reading “Hydro on the Great Lakes: preserving American history”
Coast Survey finds historic City of Chester wreck, again
NOAA announced that one of Coast Survey’s navigation response teams found the underwater wreck of the passenger steamer City of Chester, which sank in 1888 in a collision in dense fog near where the Golden Gate Bridge stands today. City of Chester had just left San Francisco and was headed up the California coast to Eureka with 90 passengers on August 22, 1888, when it was struck by the steamer Oceanic. Impaled on Oceanic, which was arriving from Asia, City of Chester remained afloat for six minutes before sinking. Sixteen people died in the accident.
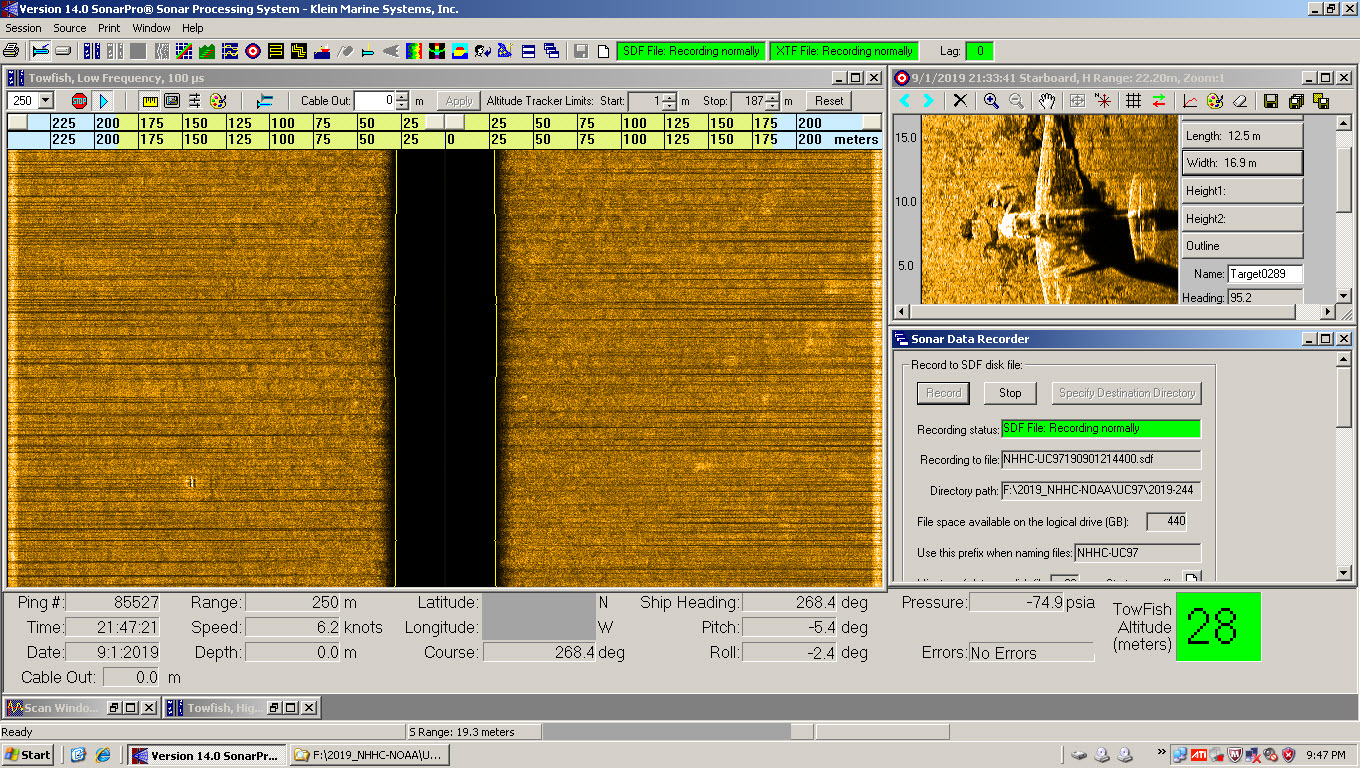
Navigation Response Team 6 (NRT6) found the wreck in May 2013 while they were conducting regular survey duties for safe navigation, assessing a potential pollution threat from the S.S. Fernstream, a wreck from 1952. Sonar images confirmed that the target was the 202-foot steamship City of Chester, sitting upright, shrouded in mud, 216 feet deep at the edge of a small undersea shoal, rising 18 feet from the seabed.

Continue reading “Coast Survey finds historic City of Chester wreck, again”
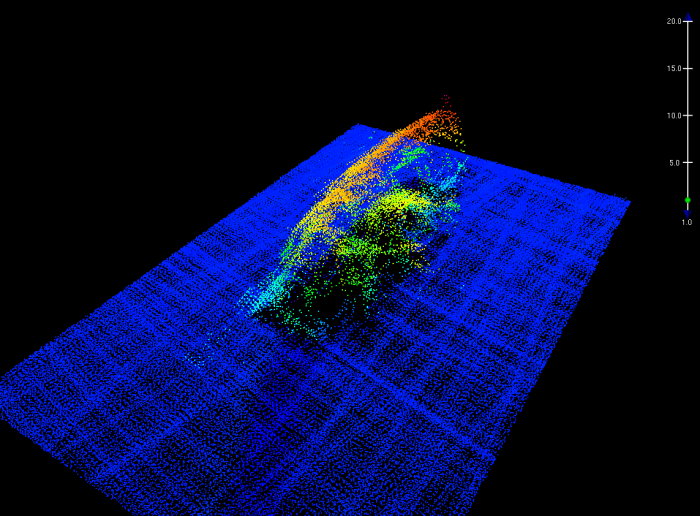
The colors of sound
The digital terrain model depicts the wreck of the freighter Fernstream, a 416-foot motor cargo vessel that sank after a collision near the entrance of the San Francisco Bay in 1952. NRT6 surveyed Fernstream as part of a recent study – identifying potential polluting shipwrecks – conducted by the Office of National Maritime Sanctuaries and the Office of Response and Restoration.
Coast Survey unveils easier access to wreck information
Maintaining documentation for features depicted on nautical charts is more complicated than you probably imagine. For instance, Coast Survey maintains information on more than 10,000 submerged wrecks and obstructions in U.S. coastal waters – and it just got easier for the public to access that free information.
Coast Survey uses our Automated Wreck and Obstruction Information System (AWOIS) to help plan hydrographic survey operations and to catalog the many reported wrecks and obstructions considered navigational hazards within U.S. coastal waters. The public also has access to this rich information source. Marine archaeologists and historians, fishermen, divers, salvage operators, and others in the marine community find AWOIS valuable as an historical record of selected wrecks and obstructions.
Continue reading “Coast Survey unveils easier access to wreck information”