UPDATE: The Nav-cast scheduled for 9/26 at 1 p.m. (EDT) is cancelled and will be rescheduled at a later date. We apologize for the inconvenience.
Join us for our next NOAA Nav-cast, a quarterly webinar series that highlights the tools and trends of NOAA navigation services.
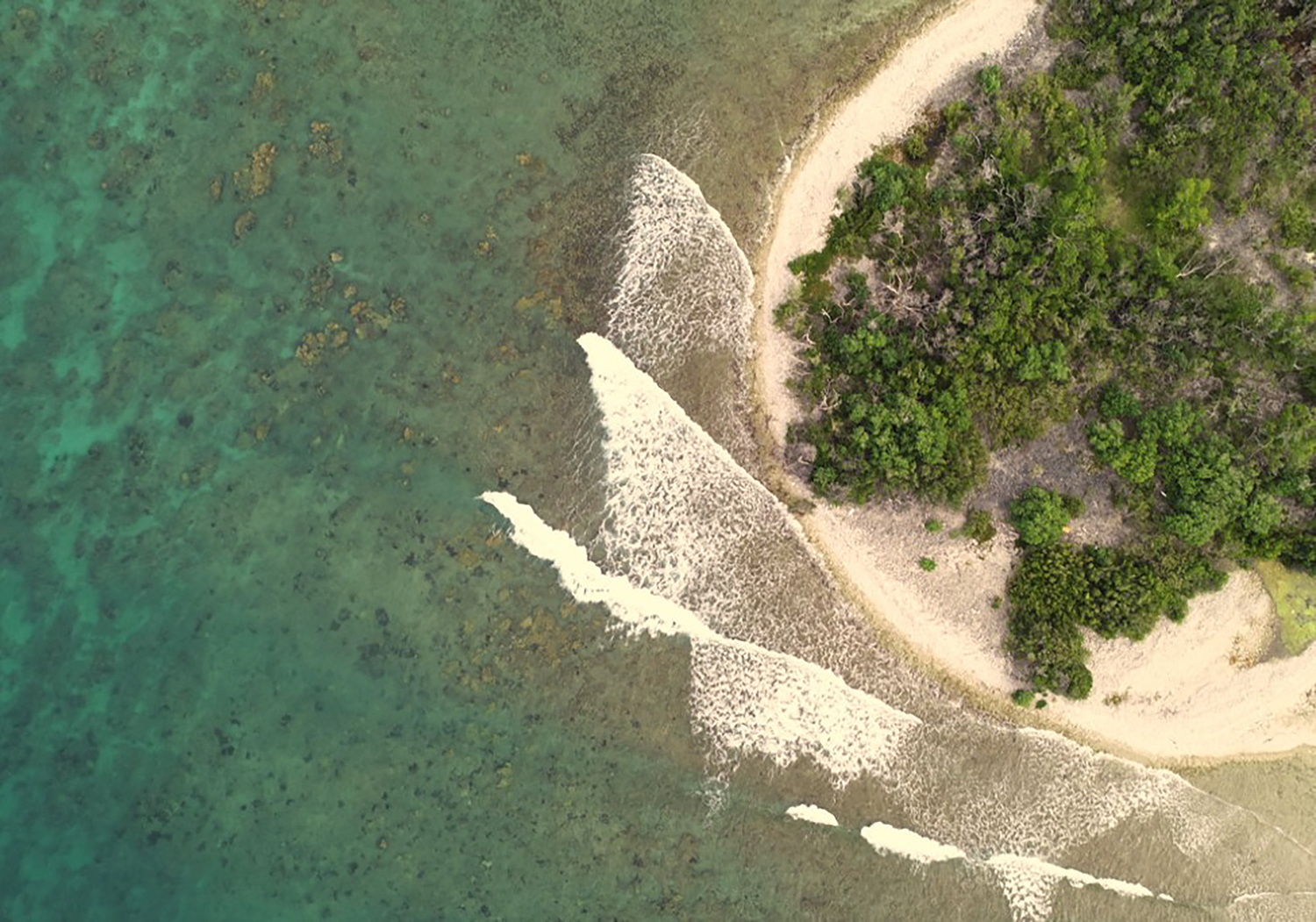
NOAA’s nowCOAST: A one-stop-shop for coastal conditions before you head out on the water
NOAA’s nowCOAST (nowcoast.noaa.gov) — a free online interactive map viewer —provides situational awareness on present and future weather and oceanographic conditions for mariners and other coastal users by integrating data from across NOAA and regional observing systems. Users can assess present conditions by creating maps of the latest in-situ weather/marine weather observations, weather radar mosaics, cloud images from GOES weather satellites, and surface wind and sea-surface temperature analyses for the last few hours. Users can also obtain maps of critical weather/marine weather advisories, watches, and warnings, weather forecasts, tropical cyclone track and intensity forecasts, and forecast guidance of water levels, water temperature, salinity, and currents from NOAA oceanographic forecast models. Users can display these maps using the nowCOAST map viewer or by connecting to its map services. nowCOAST operates in a high-availability hosting facility and is monitored 24 x 7.
Continue reading “Register for NOAA Nav-cast webinar: NOAA’s nowCOAST”