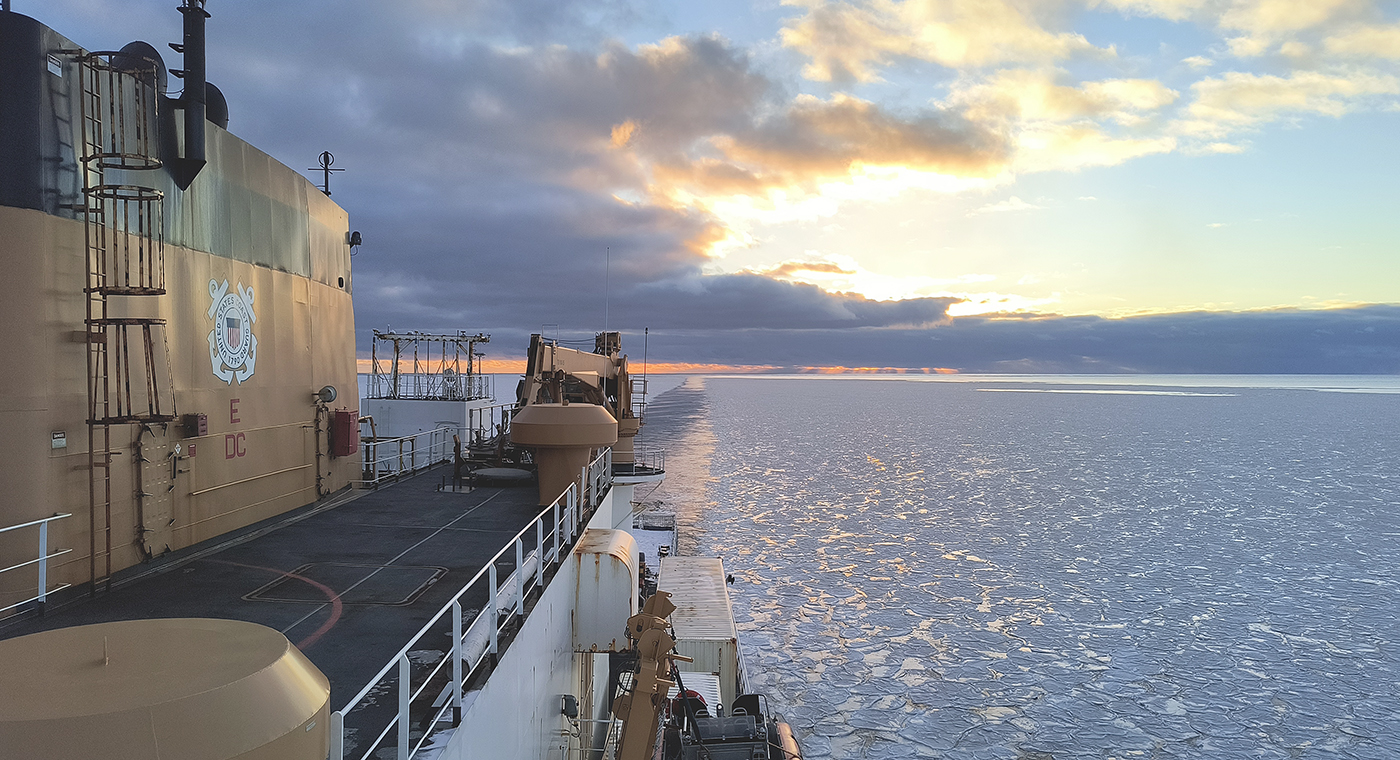
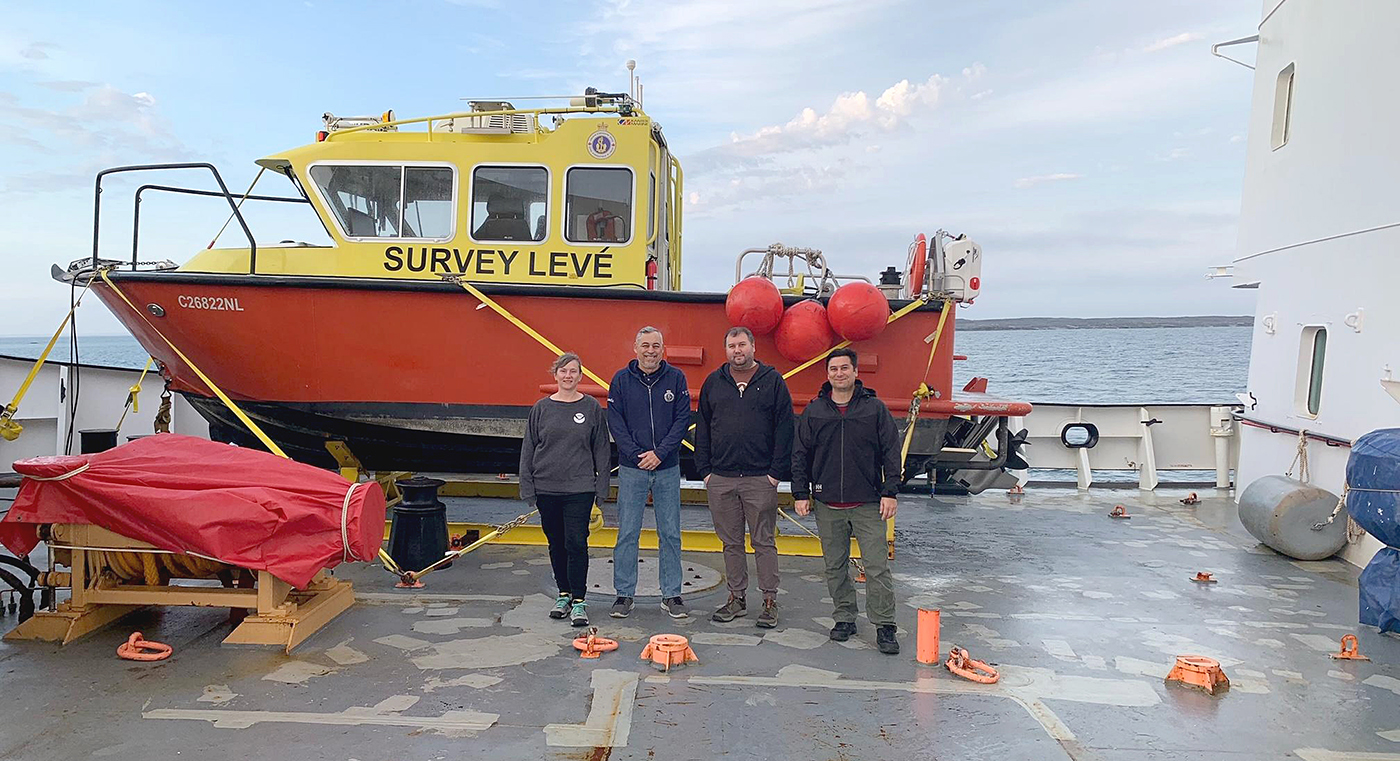
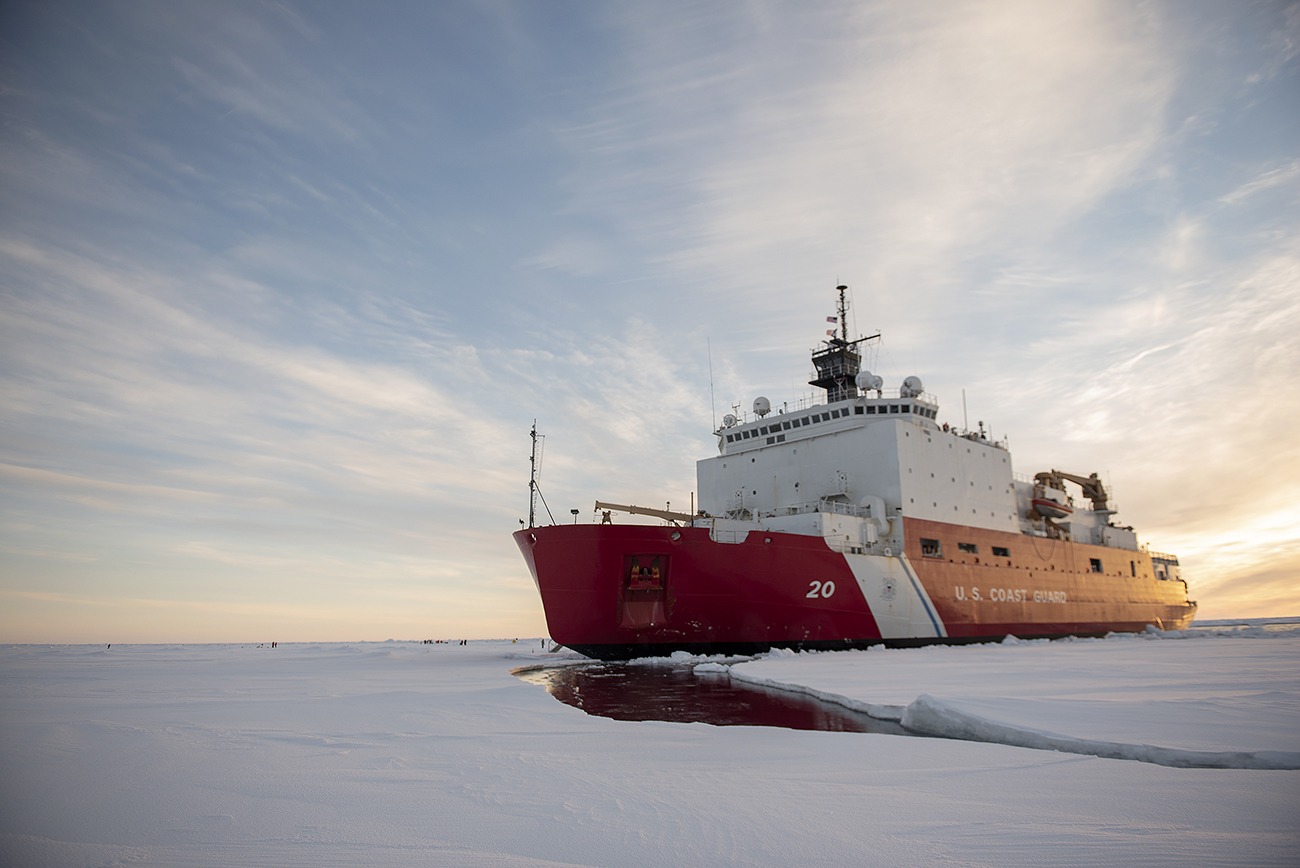
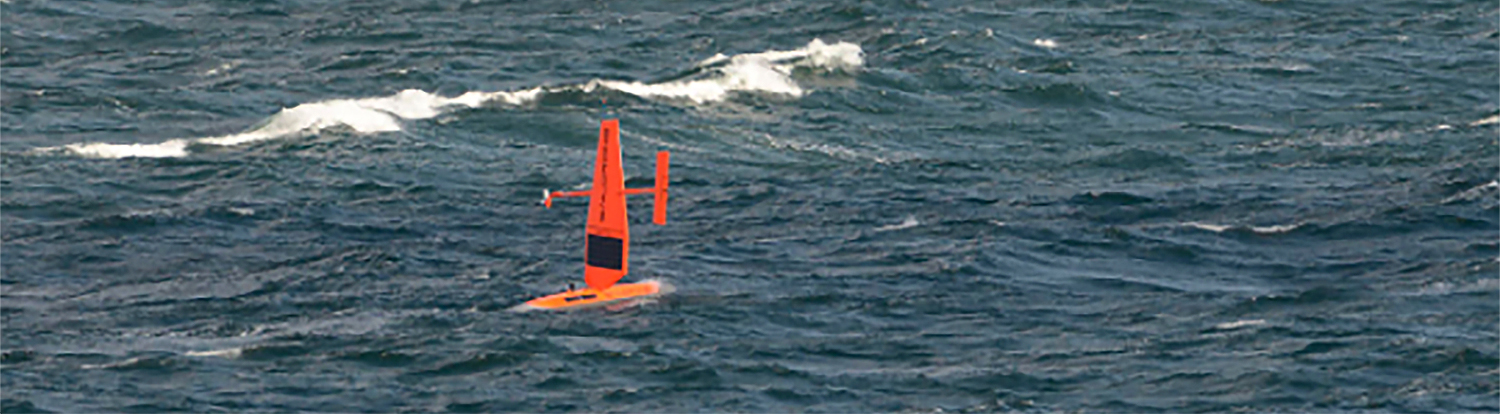
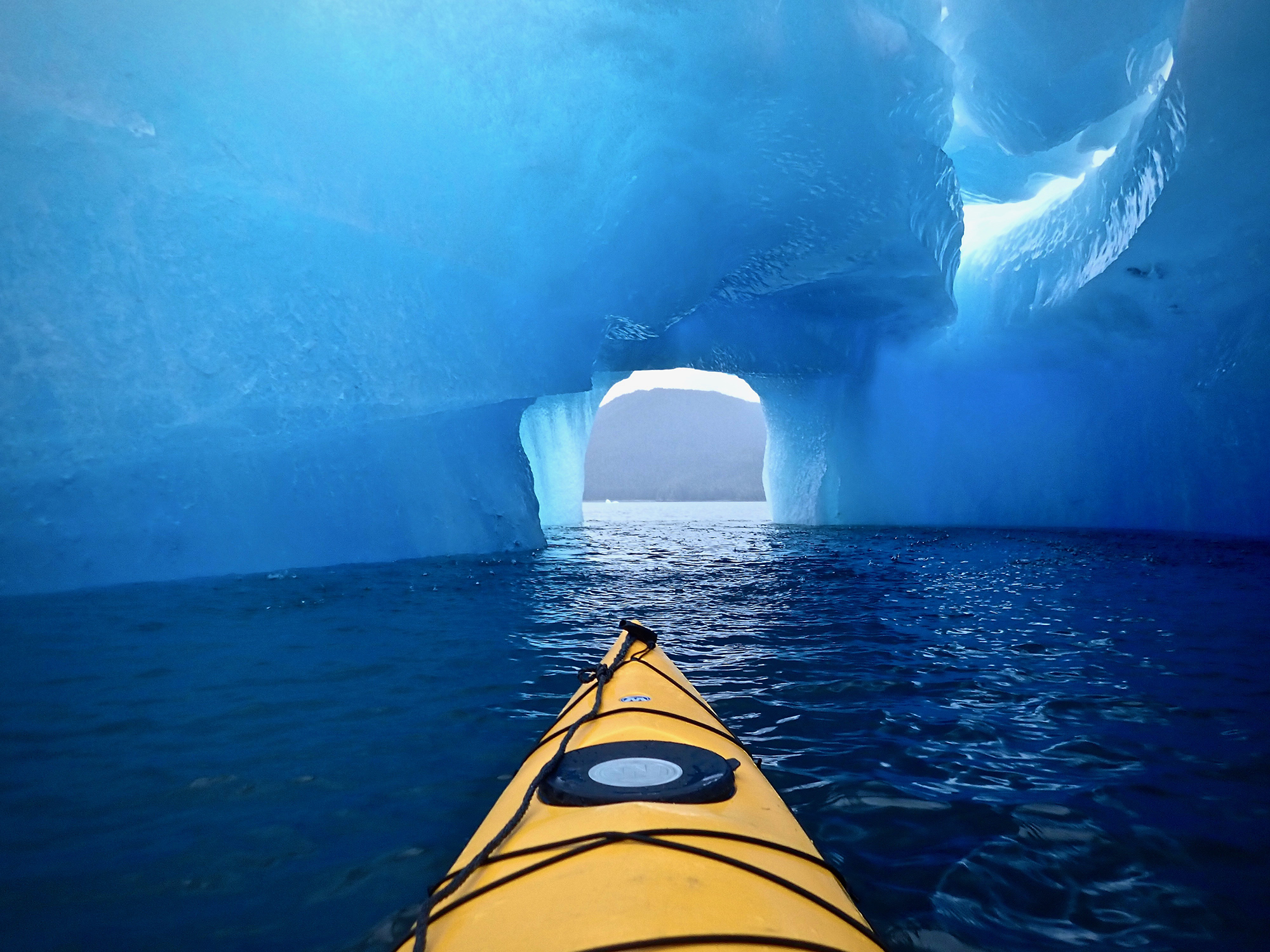
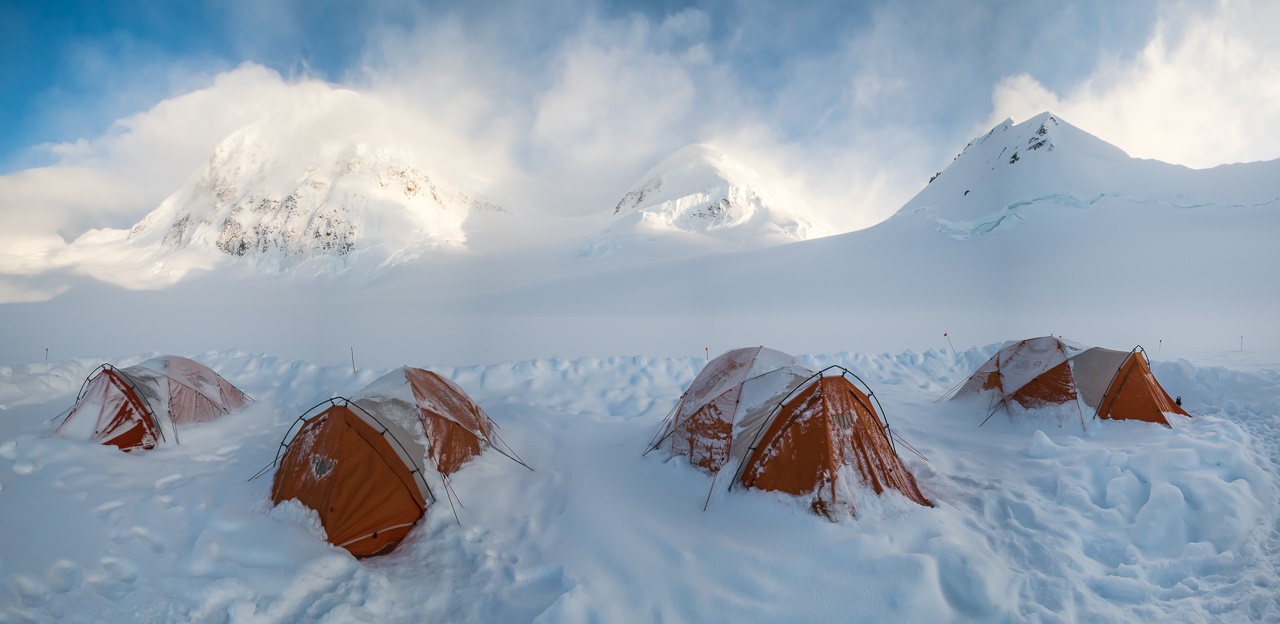
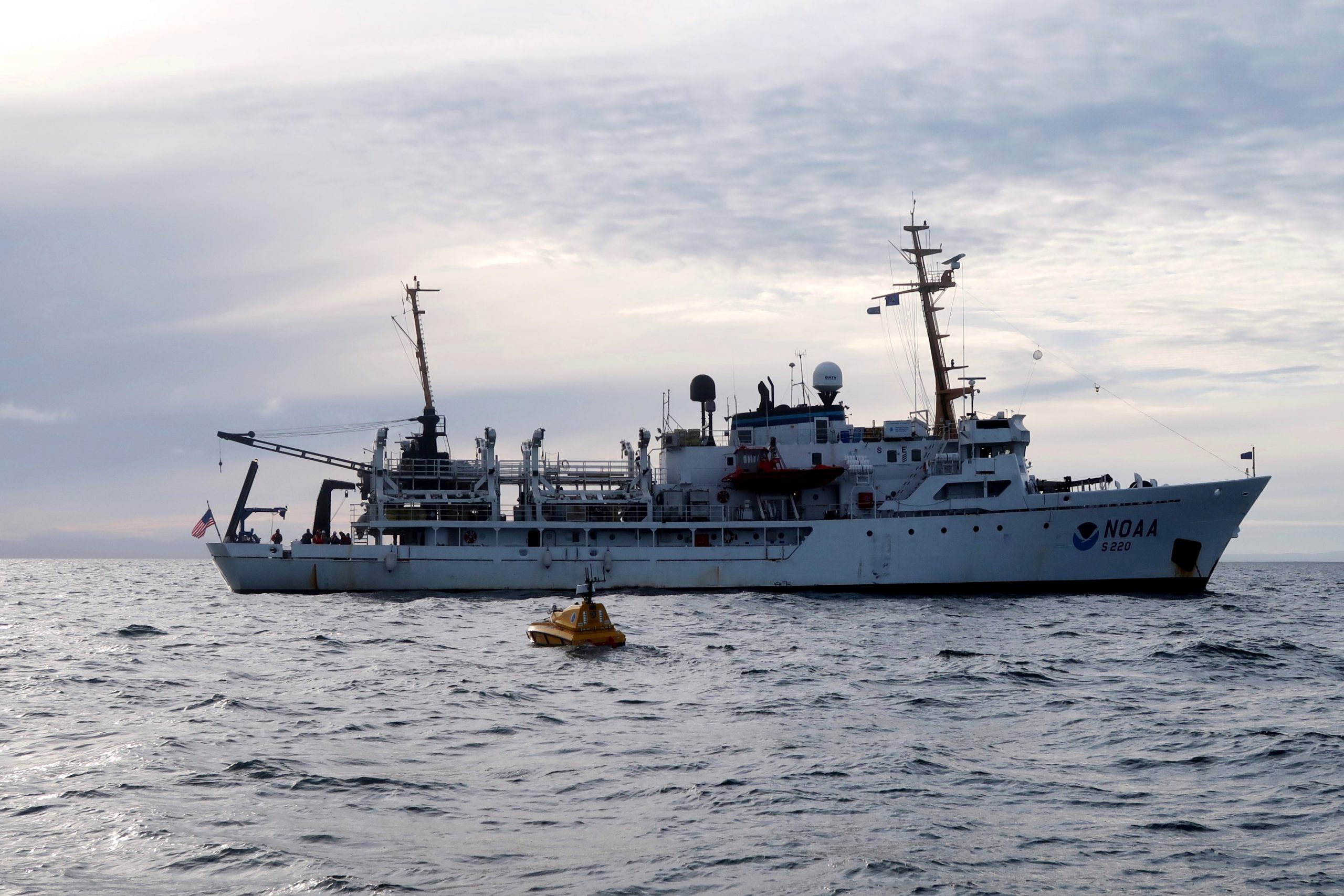
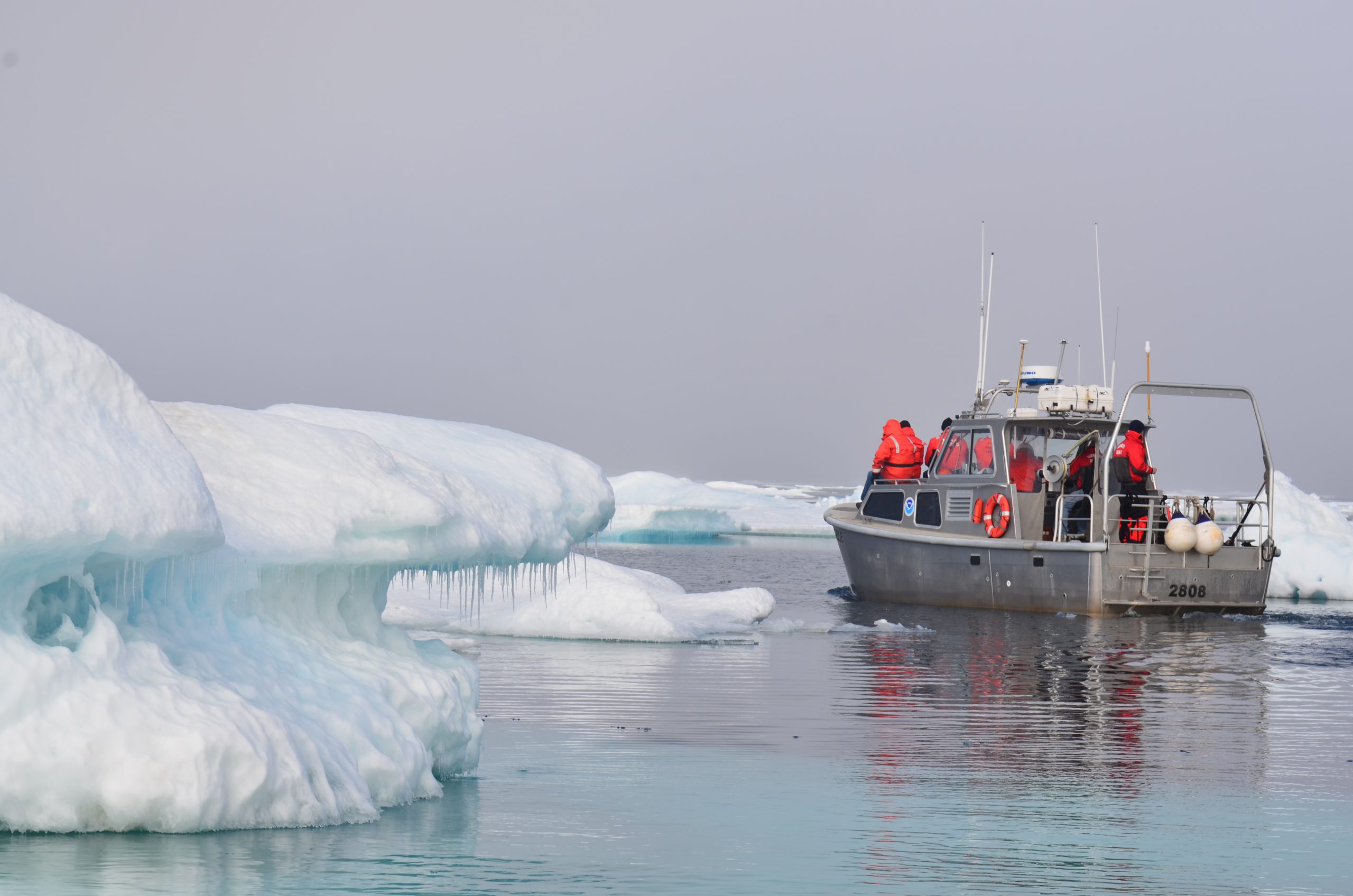
In October through early November 2024, NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey, the University of New Hampshire, U.S. National Science Foundation, and U.S. Coast Guard partnered to complete a coordinated mapping mission along the north slope of Alaska aboard the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy. Advancing the 2020 National Strategy on Ocean Mapping, Exploring, and Characterizing the U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone, the mission acquired depth data in uncharted waters along the Coast Guard-proposed Arctic shipping route, deployed a series of oceanographic buoys, and provided at sea training on interdisciplinary scientific expeditions for junior scientists. The mission capitalized on a rare opportunity to maximize data observations within a data-starved region in support of Seascape Alaska, a regional mapping campaign.
Surveying the Canadian Arctic aboard the icebreaker Henry Larsen
Annie Raymond, a member of one of NOAA’s navigation response teams, spent time in late summer aboard Canadian Coast Guard (CCG) icebreaker Henry Larsen in the Canadian Arctic with the Canadian Hydrographic Service (CHS). Her time aboard the ship was part of an exchange program designed as an opportunity for the Office of Coast Survey and CHS to gain exposure to each other’s field operations, particularly highlighting challenges for Arctic operations. Throughout the experience, she observed similarities and differences between Coast Survey and CHS data acquisitions and operations.
Continue reading “Surveying the Canadian Arctic aboard the icebreaker Henry Larsen”Alaska to Greenland via the Northwest Passage
By Lt. Patrick Debroisse
In August and September 2021, the U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy transited through the Northwest Passage, from Alaska to Greenland. This voyage provided members of the University of New Hampshire’s Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping/Joint Hydrographic Center (CCOM/JHC) the opportunity to collect data, helping to fill gaps in current hydrographic coverage in the passage and in the U.S. Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). Data in the Arctic where sea ice impedes ships is sparse. This is concerning as the Arctic nations, especially the United States, Canada, and Greenland evaluate both extended continental shelf claims and the potential for shipping routes through the Northwest Passage.
Continue reading “Alaska to Greenland via the Northwest Passage”Autonomous vessel operations in the Arctic: Lessons learned from the Summer 2020 Mapping Mission
On May 28, 2020, four uncrewed vessels departed Alameda, California, to begin their transit across the Pacific Ocean, through Unimak Pass, across the Bering Sea, and into the Arctic. These small, uncrewed vessels, powered only by wind and sun, arrived at Point Hope, Alaska, in early August to start an ambitious project acquiring new depth data along the 20 and 50 meter depth contours from Point Hope to the Canadian border. This was the start of a challenging Arctic project that would contend with weather, sea ice, and equipment failures, all while avoiding potential conflicts with indigenous subsistence hunting.
Continue reading “Autonomous vessel operations in the Arctic: Lessons learned from the Summer 2020 Mapping Mission”NOAA wants to hear from you on ocean and coastal mapping topics
There are three opportunities in the coming month to provide input to NOAA on its navigation services and the future implementation of national ocean and coastal mapping strategies, development of standard ocean mapping protocols, and precision marine navigation.
Continue reading “NOAA wants to hear from you on ocean and coastal mapping topics”Capturing scenes from hydrographic surveying
There are many benefits to working on a hydrographic survey project for NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey. Some would say having the opportunity to visit amazing landscapes, work with talented people, and collect important environmental data are just a few of them. Recently, Coast Survey’s Hydrographic Surveys Division hosted an internal photo contest inviting employees and contractors to submit images in the categories of Ships and Boats, Landscapes, People, and Data. On this Earth Day 2020, we thought we would share our contest winners with you.
Continue reading “Capturing scenes from hydrographic surveying”NOAA releases 2019 hydrographic survey plans
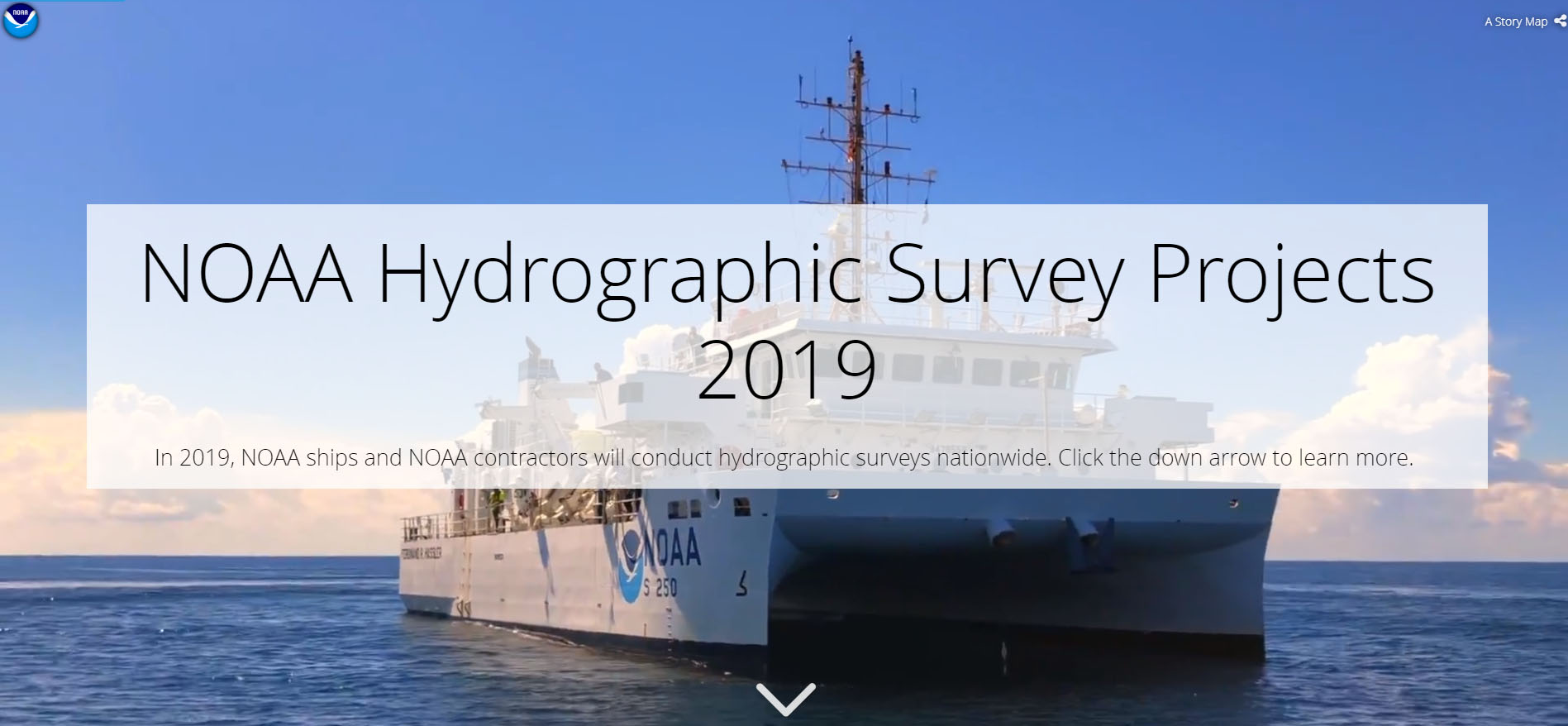
NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey is the nation’s nautical chartmaker, and maintains a suite of more than a thousand nautical charts. Coast Survey is responsible for charting U.S. waters and Great Lakes covering 3.4 million square nautical miles (SNM) of water and 95,000 miles of coastline.
NOAA’s hydrographic survey ships along with hydrographic contractor vessels, recently kicked off the 2019 hydrographic survey season. These surveys not only update the suite of nautical charts, but also help to maintain the safety of maritime commerce, recreational boaters, natural ecosystems, and much more. Operations are scheduled for maritime priority areas around the country and are outlined in Coast Survey’s “living” story map. Here is a list of where they are headed this year:
Continue reading “NOAA releases 2019 hydrographic survey plans”From NOAA Ship Fairweather to Mt. Fairweather: Commanding officer summits ship’s namesake
By Cmdr. Mark Van Waes, former commanding officer of NOAA Ship Fairweather
Mount Fairweather stands tall above Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve, dominating the skyline for miles around (when weather permits visibility). Only about 12 miles inshore from the Gulf of Alaska and soaring to 15,325 feet, it is one of the highest coastal peaks in the world.
Continue reading “From NOAA Ship Fairweather to Mt. Fairweather: Commanding officer summits ship’s namesake”
NOAA researches autonomous survey system in the Arctic
By Rob Downs, Office of Coast Survey unmanned systems projects lead
A team composed of research engineers and a graduate student from the University of New Hampshire Center for Coastal and Ocean Mapping/Joint Hydrographic Center (UNH CCOM/JHC) and personnel from NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey are aboard the NOAA Ship Fairweather to test UNH’s BEN (Bathymetric Explorer and Navigator) unmanned surface vehicle (USV). On Saturday, July 28, the Fairweather made the first successful launch of a USV for an operational hydrographic survey from a NOAA vessel in the Arctic. The team conducted four additional deployments, including an extended overnight survey made in coordination with the ship.
Continue reading “NOAA researches autonomous survey system in the Arctic”
NOAA surveys the unsurveyed, leading the way in the U.S. Arctic
President Thomas Jefferson, who founded Coast Survey in 1807, commissioned Lewis and Clark’s Corps of Discovery Expedition in 1803, the first American expedition to cross the western portion of the contiguous United States. Today there remains a vast western America territory that is largely unknown and unexplored – the U.S. waters off the coast of Alaska. As a leader in ocean mapping, NOAA Coast Survey launches hydrographic expeditions to discover what lies underneath the waves.
Alaska is one-fifth the size of the contiguous United States, and has more than 33,000 miles of shoreline. In fact, the Alaskan coast comprises 57 percent of the United States’ navigationally significant waters and all of the United States’ Arctic territory. Alaskan and Arctic waters are largely uncharted with modern surveys, and many areas that have soundings were surveyed using early lead line technology from the time of Capt. Cook, before the region was part of the United States. Currently only 4.1 percent of the U.S. maritime Arctic has been charted to modern international navigation standards. Continue reading “NOAA surveys the unsurveyed, leading the way in the U.S. Arctic”