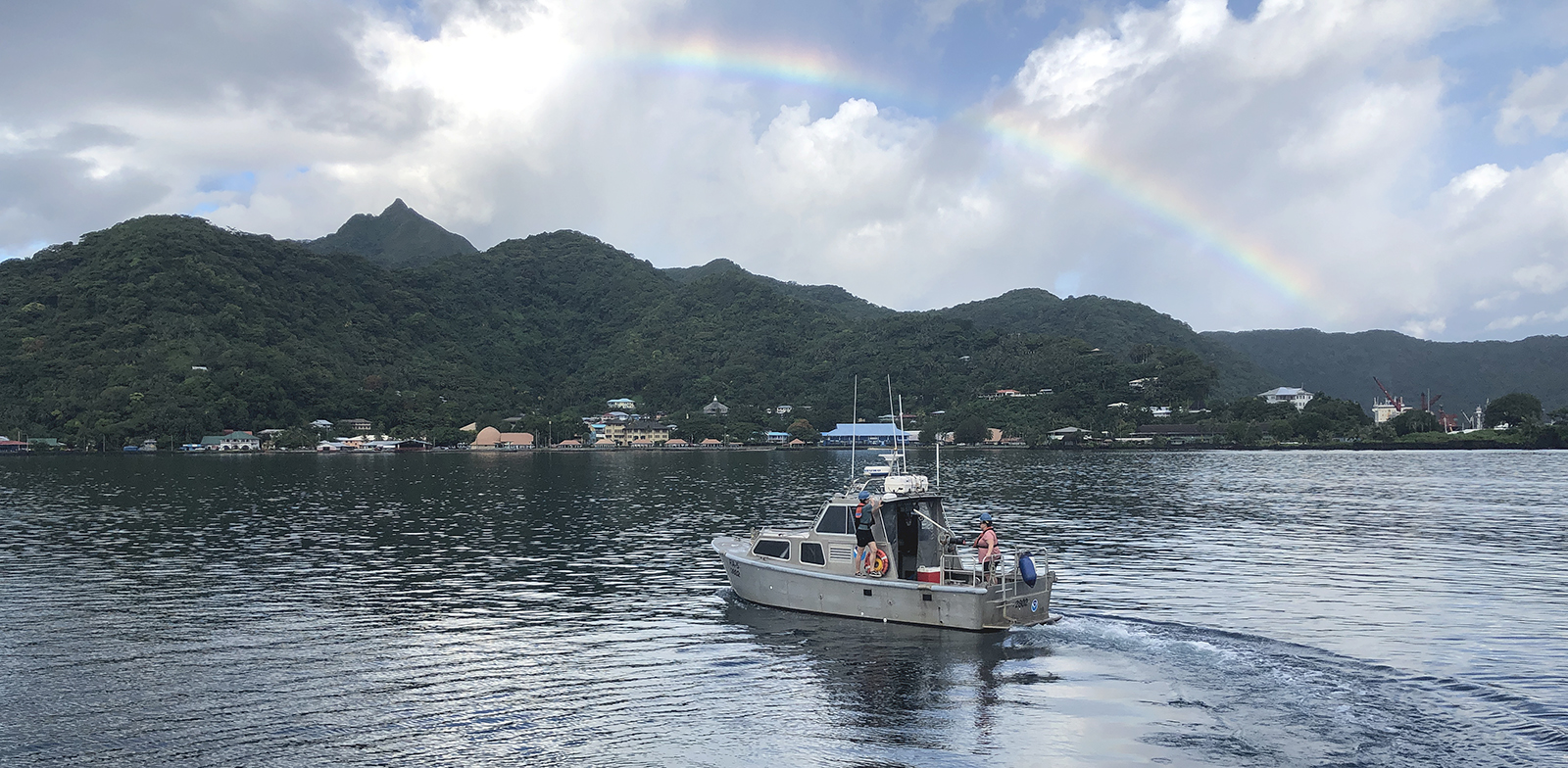
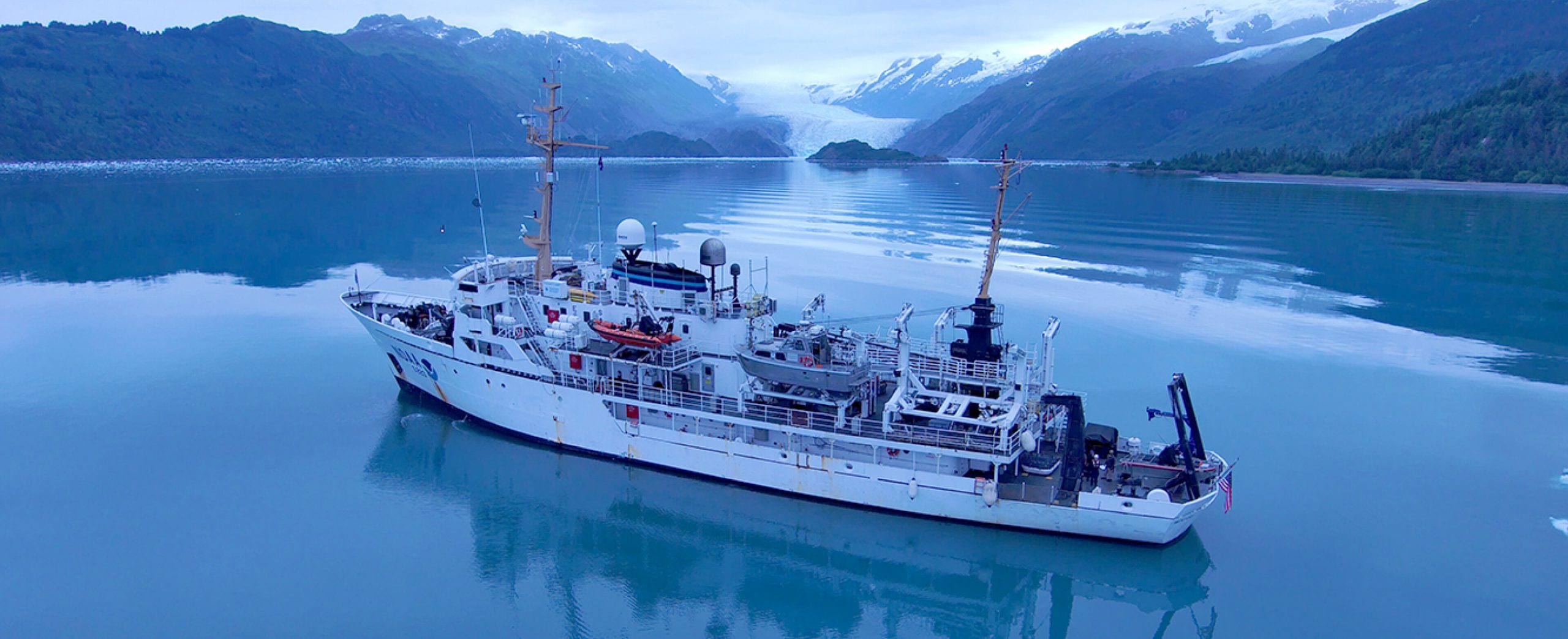
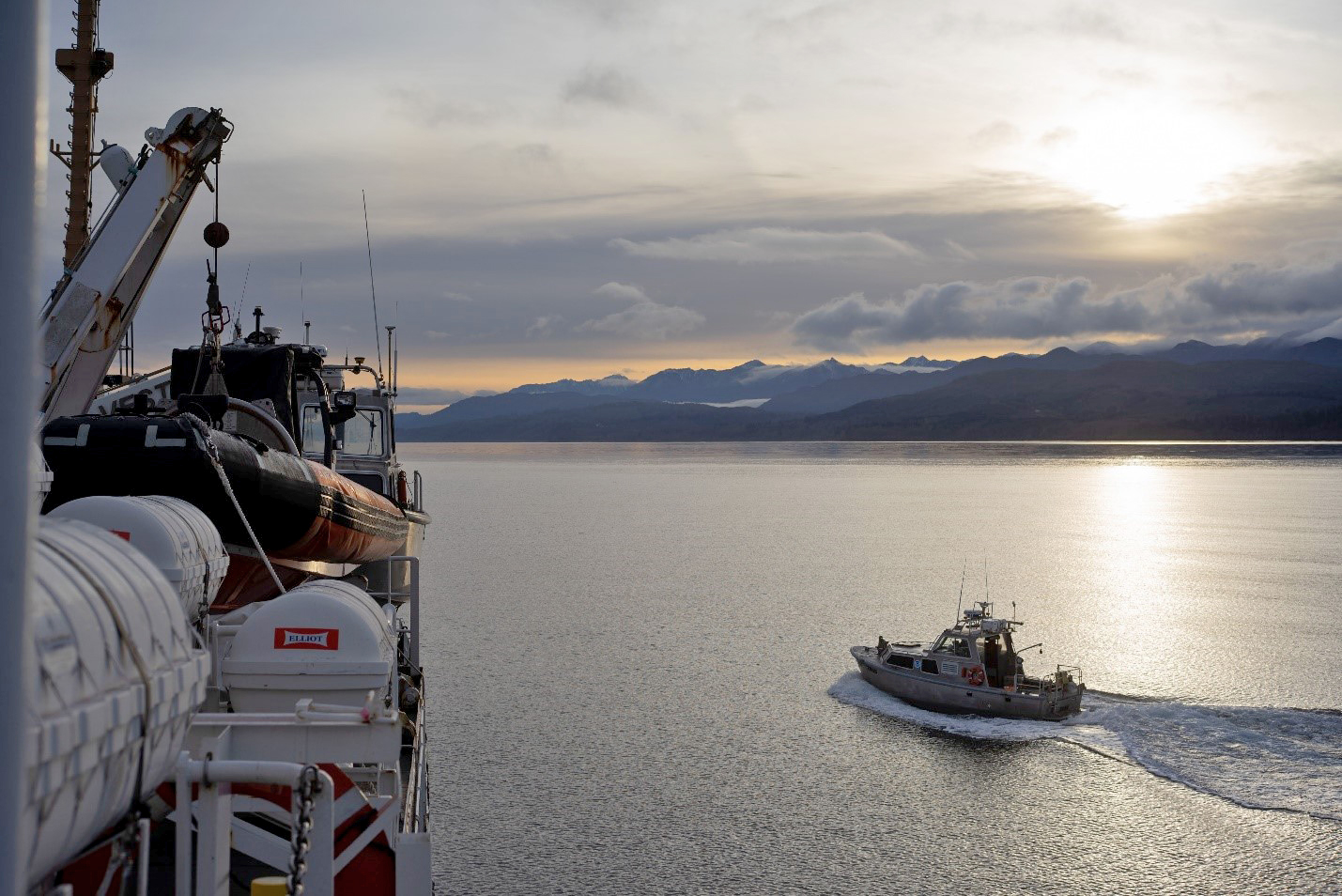
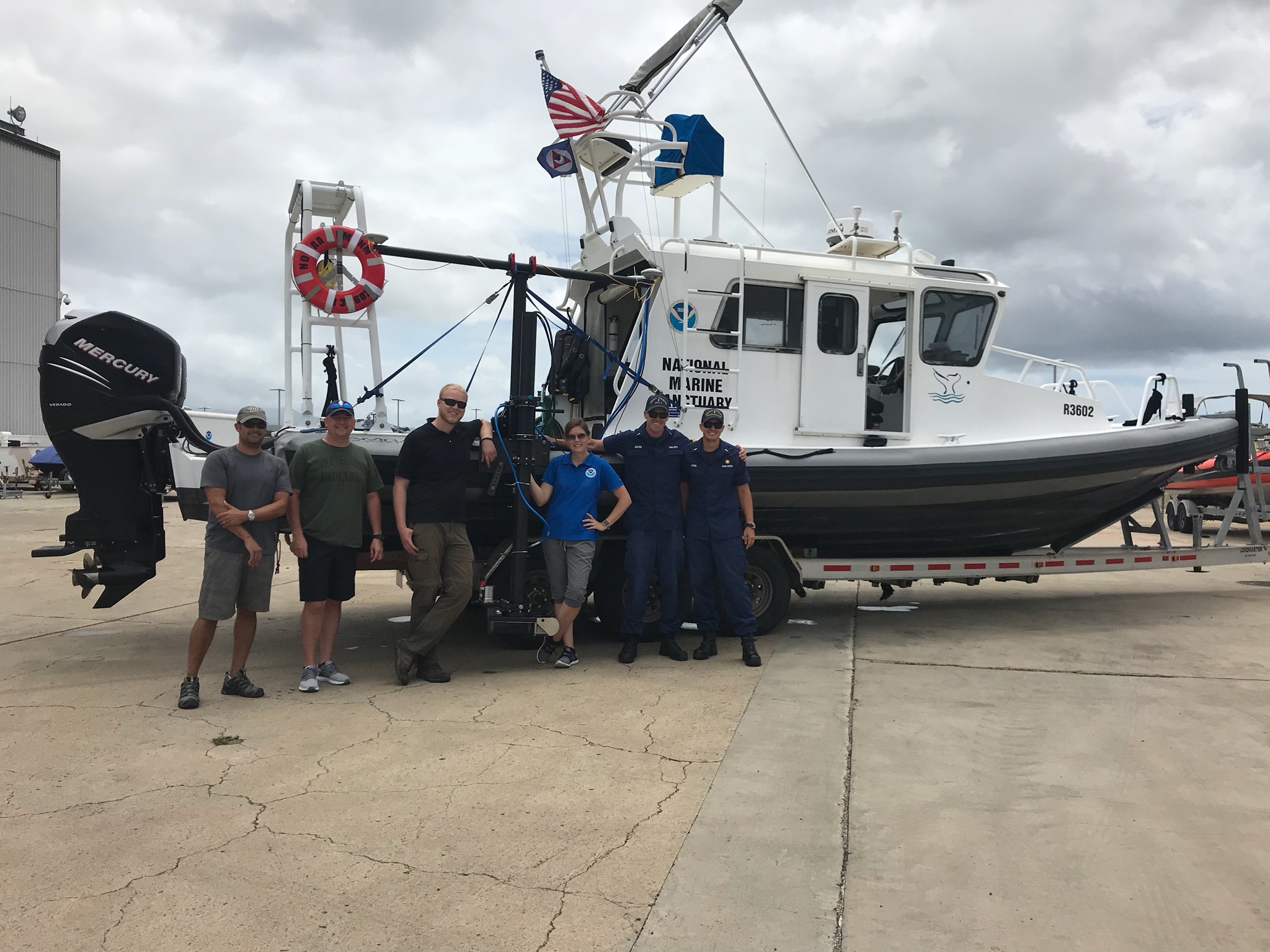
The winter months represent an end to NOAA’s active survey season. During this period, hydrographic survey ships, navigation response team survey vessels, and contractor teams and vessels undergo maintenance and repair in anticipation of the upcoming survey season. NOAA’s 2025 survey season will begin soon as planned survey projects go through the planning and development process and begin to filter to the forefront of each field party’s focus. The ships and survey vessels collect bathymetric data (i.e. map the seafloor) to support nautical charting, modeling, and research, but also collect other environmental data to support a variety of ecosystem sciences. NOAA considers hydrographic survey requests from stakeholders such as marine pilots, local port authorities, the Coast Guard, and the boating community, and also considers other hydrographic and NOAA science priorities in determining where to survey and when. Visit our “living” ArcGIS StoryMap to find out more about our mapping projects and if a hydrographic vessel will be in your area this year!
Continue reading “NOAA’s 2025 hydrographic survey season is gearing up and will be underway soon”NOAA’s 2024 hydrographic survey season is underway
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s 2024 hydrographic survey season is ramping up and will be in full swing before too long. For the past few months, NOAA hydrographic survey ships, navigation response teams, and contractors have been diligently preparing for the upcoming field season. The ships and survey vessels collect bathymetric data to support nautical charting, modeling, and research, but also collect other environmental data to support a variety of ecosystem sciences. NOAA considers hydrographic survey requests from stakeholders such as marine pilots, local port authorities, the Coast Guard, and the boating community, and also considers other hydrographic and NOAA science priorities in determining where to survey and when. Visit our “living” ArcGIS StoryMap to find out more about our mapping projects and if a hydrographic vessel will be in your area this year!
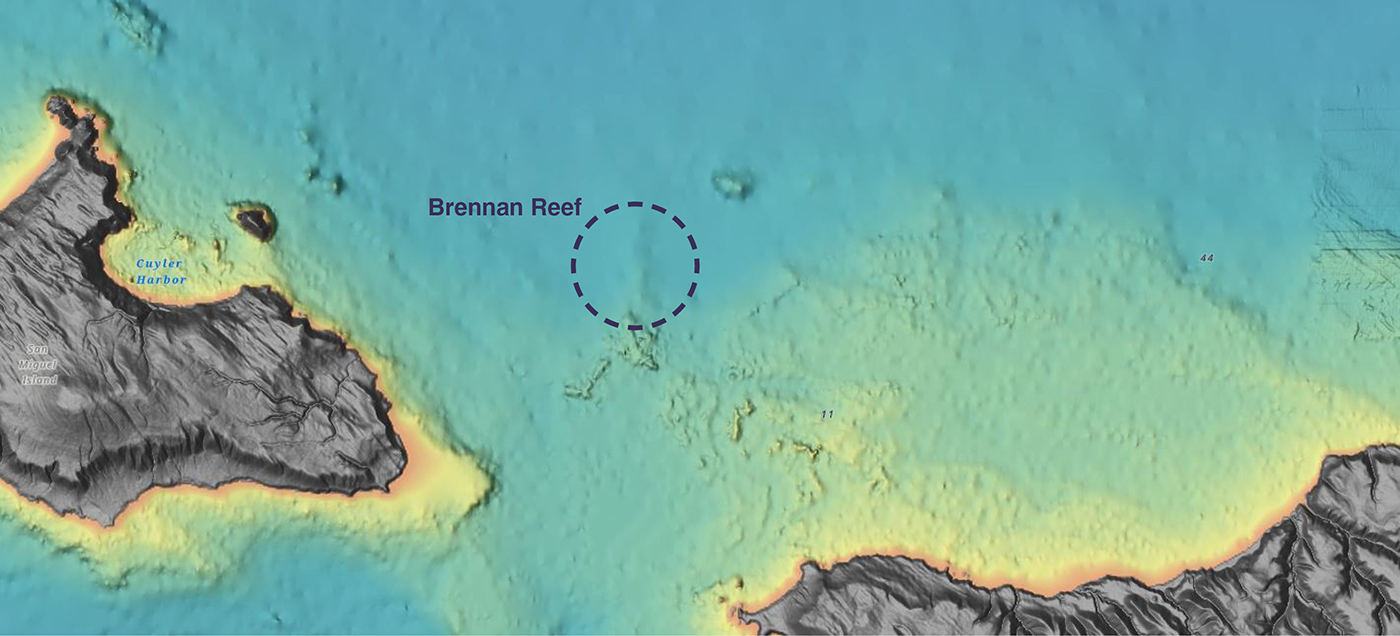
Continue reading “NOAA’s 2024 hydrographic survey season is underway”Naming Brennan Reef, a previously uncharted pinnacle in Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary
NOAA Corps Rear Adm. Richard T. “Rick” Brennan, recent director of NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey, was deeply dedicated to NOAA’s mission and was an integral part of building connections across NOAA programs to benefit coastal communities around the United States. One example of Rick’s leadership was the Southern California Seafloor Mapping Initiative, a partnership between Coast Survey, Office of National Marine Sanctuaries (ONMS), National Centers for Coastal Ocean Science (NCCOS) and National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS). Among many important accomplishments of this coordinated mapping effort was the survey of a previously uncharted reef in Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary. Through legislative action led by U.S. Congressman Salud Carbajal of California’s 24th District, this reef has been officially designated as “Brennan Reef.”
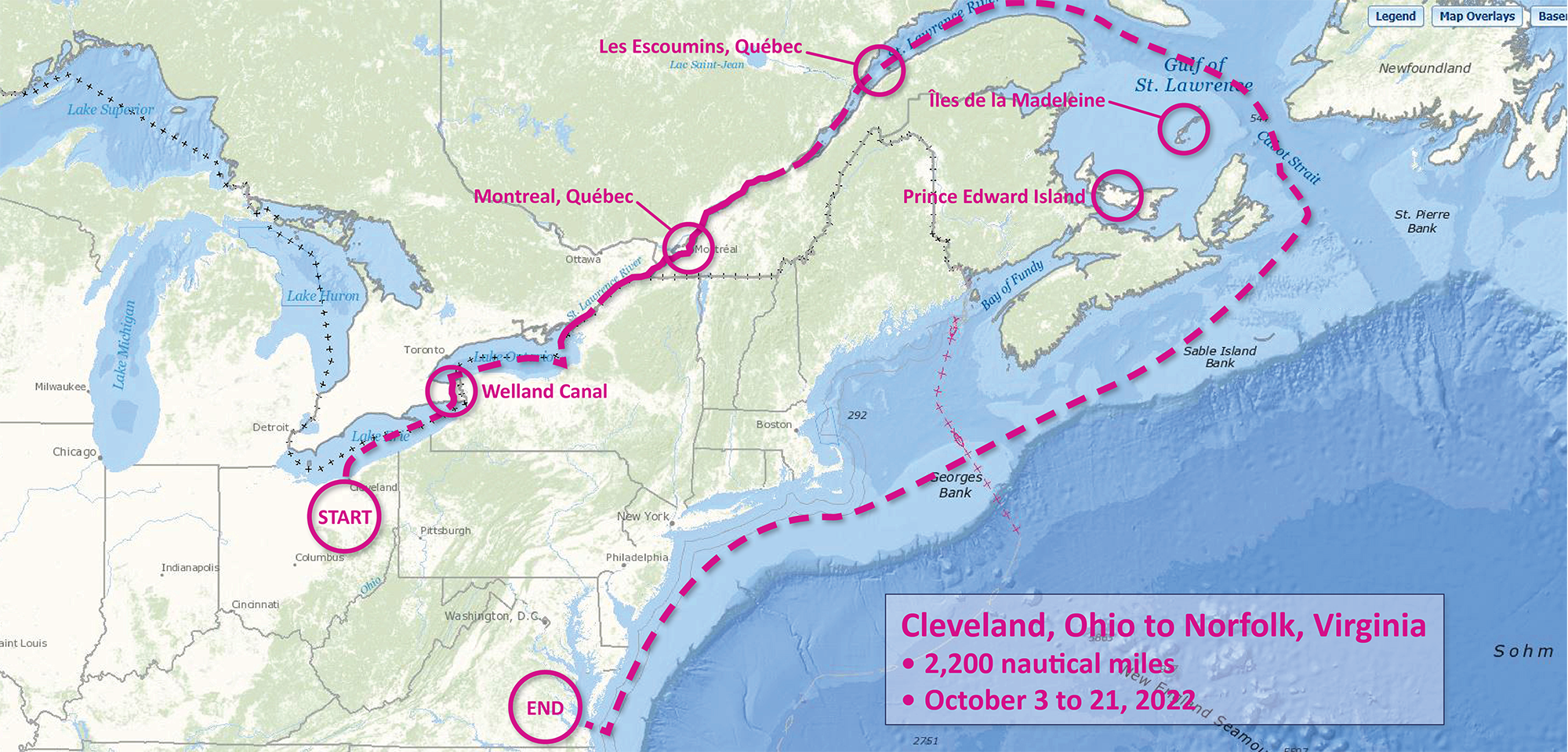
Continue reading “Naming Brennan Reef, a previously uncharted pinnacle in Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary”NOAA Ship Thomas Jefferson completes productive field season in the Great Lakes
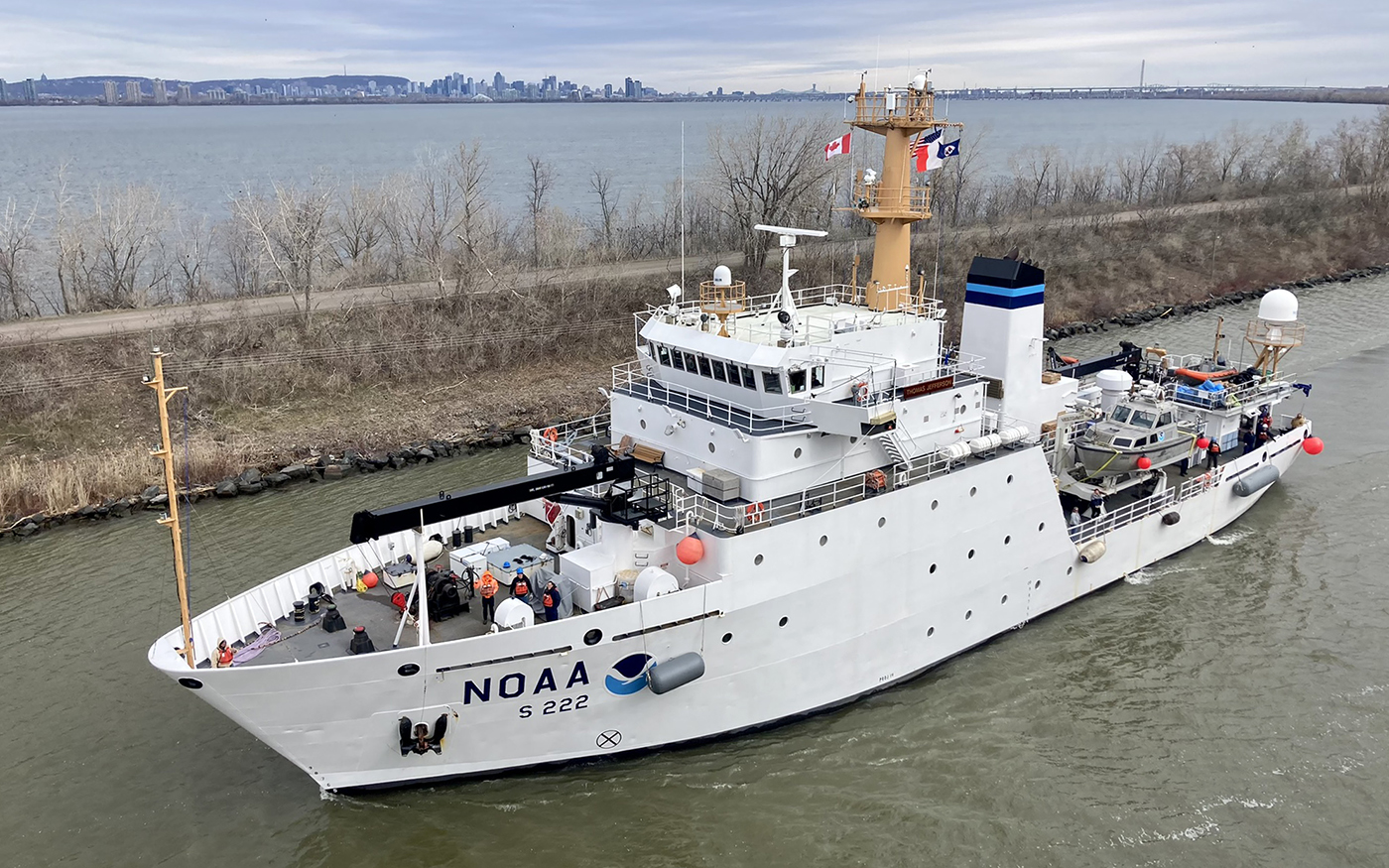
Although NOAA has a significant presence in the Great Lakes, this is the first time a white-hulled NOAA hydrographic ship has deployed there since the early 1990s. As a result of survey work in the Great Lakes, NOAA Ship Thomas Jefferson surveyed 450 square nautical miles of lake bottom in Lake Erie – an economically important and ecologically sensitive region. The ship also surveyed 274 square nautical miles in Lake Ontario in October. In both lakes, there were 42 confirmed and new shipwrecks identified along with 22 additional features!
Continue reading “NOAA Ship Thomas Jefferson completes productive field season in the Great Lakes”NOAA focuses on the Great Lakes for the 2022 field season
In 2022, NOAA and NOAA contractors will survey U.S. coastal waters and beyond, including multiple missions in the Great Lakes. As the volume, value and size of marine vessels in U.S. waters continues to grow, it is essential that NOAA increase the accuracy and frequency of surveys. A great amount of data on nautical charts of the Great Lakes is more than 50 years old, and only about 5 to 15 percent of the Great Lakes are mapped to modern standards using remote sensing methods such as light detection and ranging and sound navigation and ranging.
Continue reading “NOAA focuses on the Great Lakes for the 2022 field season”NOAA releases 2022 hydrographic survey season plans
NOAA hydrographic survey ships and contractors are preparing for the 2022 hydrographic survey season in U.S. coastal waters and beyond. The ships collect bathymetric data (i.e. map the seafloor) to support nautical charting, modeling, and research, but also collect other environmental data to support a variety of ecosystem sciences. NOAA considers hydrographic survey requests from stakeholders such as marine pilots, local port authorities, the Coast Guard, and the boating community, and also considers other hydrographic and NOAA science priorities in determining where to survey and when. Visit our “living” story map to find out more about our mapping projects and if a hydrographic vessel will be in your area this year!
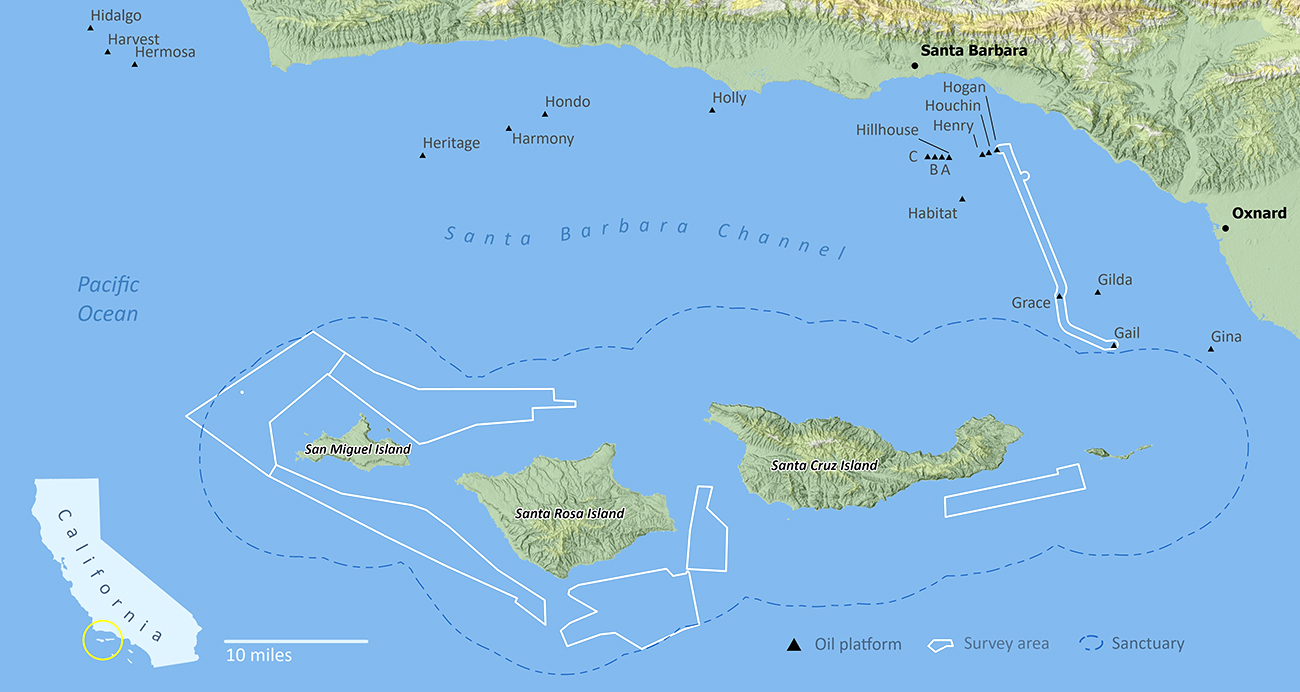
Continue reading “NOAA releases 2022 hydrographic survey season plans”Backscatter and oil platforms – a Channel Islands adventure
By HAST Bailey Schrader, Operations Officer Lt. Shelley Devereaux and HST Adriana Varchetta
After enjoying the California sunshine in San Francisco Bay, NOAA Ship Fairweather began its transit down the coast towards Santa Barbara, California. The ship would not anchor for the next sixteen days, leaving all crew on 24-hour rotations. Thankfully, the already attenuated crew was visited by augmenting scientists and hydrographers – Physical Scientist Devereaux from the Pacific Hydrographic Branch, HHST Arboleda from NOAA Ship Thomas Jefferson, and HAST Schrader from NOAA Ship Rainier. Together, they traveled south to complete one of the last projects of the season, the area in and around Channel Islands National Marine Sanctuary.
Continue reading “Backscatter and oil platforms – a Channel Islands adventure”Surveying in the Strait of Juan de Fuca during a global pandemic
By Ensign Jessie Spruill and Hydrographic Senior Survey Technician Simon Swart, NOAA Ship Fairweather
Last Thanksgiving, the crew of NOAA Ship Fairweather were busy surveying in one of the country’s busiest waterways. A global maritime entryway to the Pacific Northwest, the Strait of Juan de Fuca sees over 8,000 transits of deep-draft container ships, cargo and chemical carriers, oil tankers, and barges coming to and from Puget Sound and Canada. In addition to industrial shipping, the Strait of Juan de Fuca also supports over 200,000 transits of recreational vessels and Washington State Ferries. Located north of the Olympic Peninsula, the Strait forms the northwestern most border between the contiguous U.S. and Canada. On the American side, the region is home to eight million people including 50 First Nation communities with centuries old cultural ties to traditional fishing.
Continue reading “Surveying in the Strait of Juan de Fuca during a global pandemic”NOAA joins federal and state partners in signing MOU on emergency maritime response in Hawaii
NOAA’s Office of Coast Survey, United States Coast Guard (USCG) Sector Honolulu, State of Hawaii Department of Transportation and United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) Honolulu Division established a memorandum of understanding (MOU) outlining each signatory’s area of responsibility in the event of a disaster in the Hawaii region. The intent of the MOU is to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of response efforts and speed the reopening of the ports and waterways following an emergency.
Continue reading “NOAA joins federal and state partners in signing MOU on emergency maritime response in Hawaii”NOAA releases 2020 hydrographic survey season plans
NOAA hydrographic survey ships and contractors are preparing for the 2020 hydrographic survey season. The ships collect bathymetric data (i.e. map the seafloor) to support nautical charting, modeling, and research, but also collect other environmental data to support a variety of ecosystem sciences. NOAA considers hydrographic survey requests from stakeholders such as marine pilots, local port authorities, the Coast Guard, and the boating community, and also consider other hydrographic and NOAA science priorities in determining where to survey and when. Visit our “living” story map to find out more about our mapping projects and if a hydrographic vessel will be in your area this year!
Continue reading “NOAA releases 2020 hydrographic survey season plans”