By Ens. Lyle I. Robbins
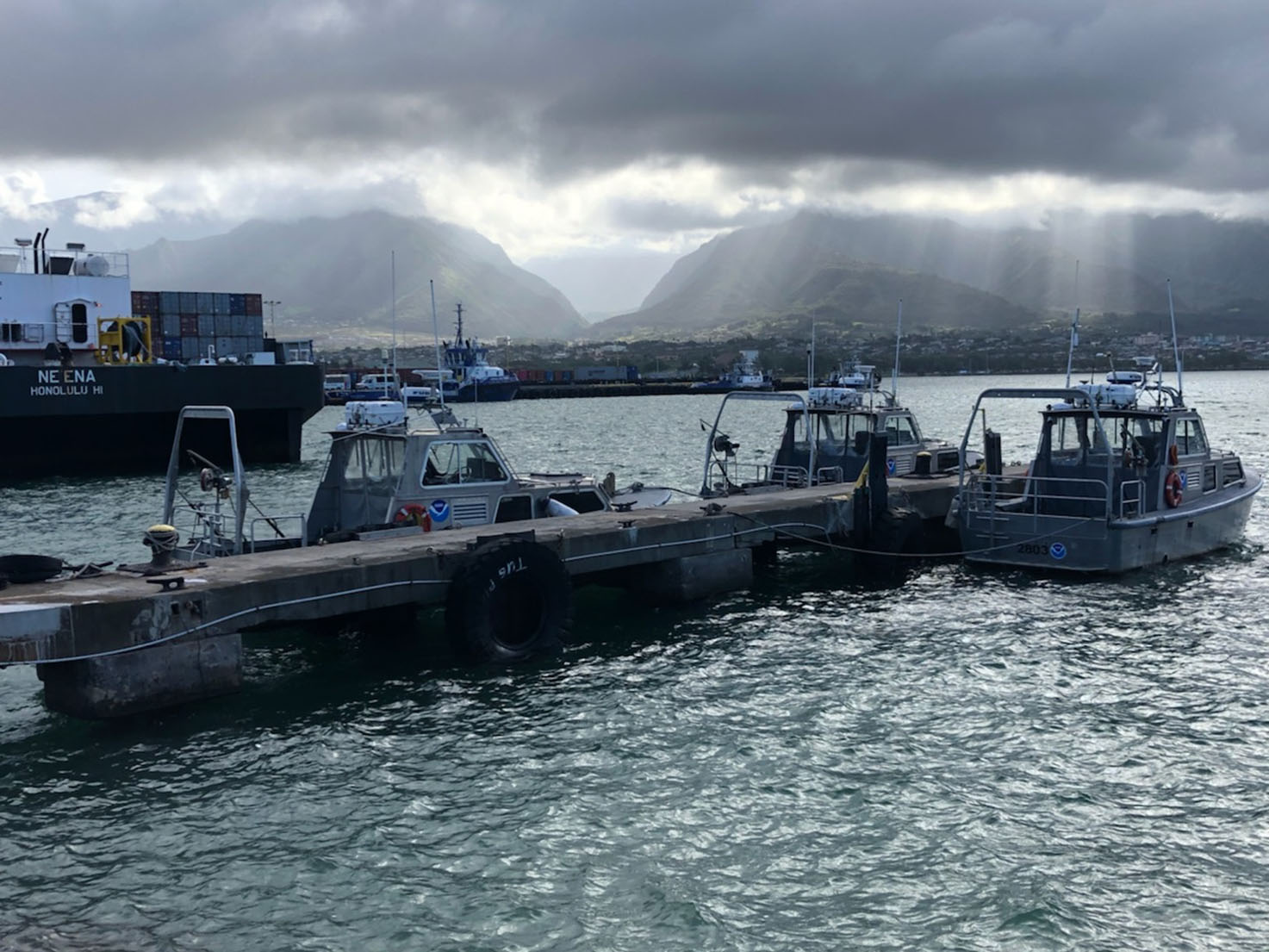
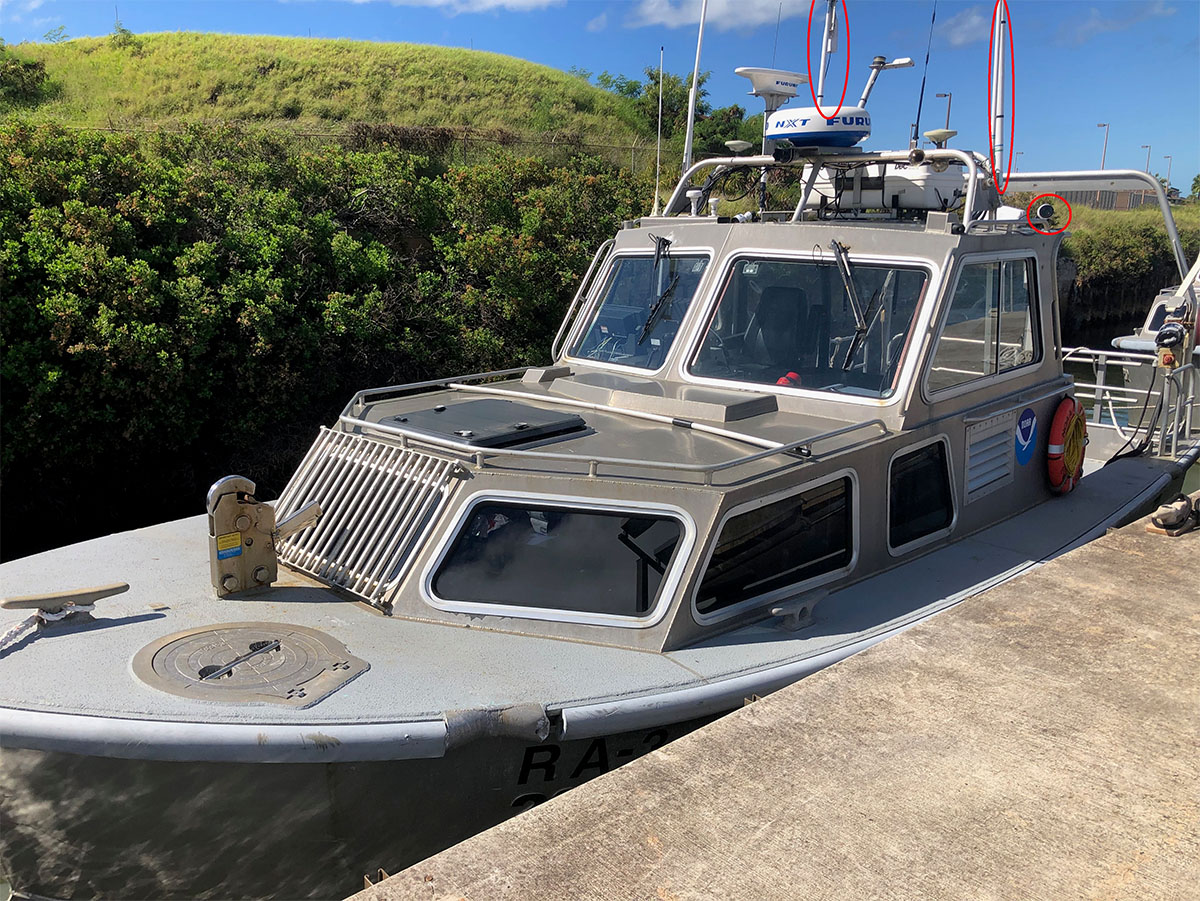
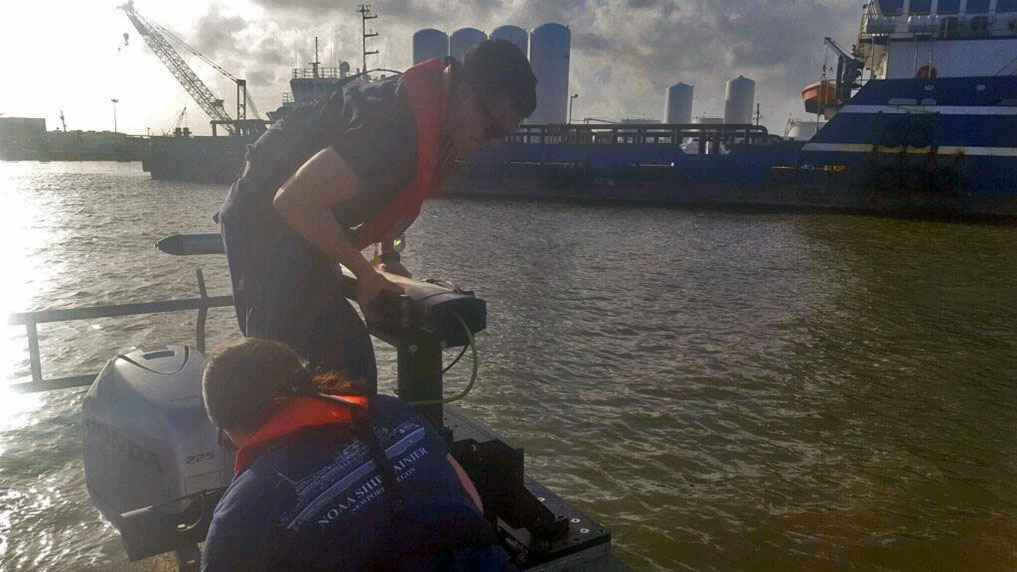
For more than 50 years, NOAA Ship Rainier and its hydrographic survey launches have surveyed the Pacific seafloor. During this time, Rainier sailed thousands of miles, including the entire U.S. west coast, Alaska, and Hawaii. This year, Rainier expands on its traditional role of hydrographic survey and is supporting dive operations in the Northwest Hawaiian Islands and in the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument. While Rainier is sailing these remote coral atolls, the survey launches — that are usually in its davits and deployed directly from the ship — are tasked to their own surveys around the islands of Maui, Moloka’i, and O’ahu.
Continue reading “Hawaiian island surveys will update nautical charts and support habitat mapping efforts”